Dartford Warbler
Curruca undata (Boddaert, 1783)
DW
 DARWA
DARWA  12620
12620

Family: Passeriformes > Sylviidae
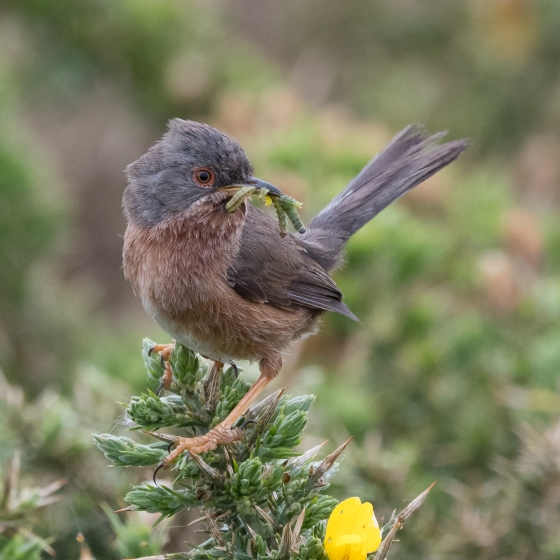

This small warbler has come back from the brink of extinction in the UK in the last 50 years.
Dartford Warblers have a relatively restricted breeding and wintering range in southern and eastern England, southern Wales and the Channel Islands. They are not found in Scotland or on the island or Ireland. Susceptible to cold weather, the harsh winter of 1962/63 compounded problems caused by habitat loss, and led to the near-extinction of this species in the UK, with just 10 pairs left in Dorset. Numbers have gradually recovered since, thanks in part of conservation interventions to protect and restore the lowland heath habitats on which Dartford Warblers rely. The species is on the UK Amber List.
Dartford Warblers are long-tailed birds, with a grey-brown head, body and wings, a distinctive red eye-ring and a russet breast. In the breeding season, they can sometimes be spotted singing from the top of Gorse bushes, but can also be seen flitting between tufts of heather. A ground-nesting species, female Dartford Warblers may lay up to three clutches a year. Dartford Warblers largely eat small invertebrate prey.
Identification
Dartford Warbler identification is usually straightforward.
SONGS AND CALLS
Listen to example recordings of the main vocalisations of Dartford Warbler, provided by xeno-canto contributors.
Call
Song
Develop your bird ID skills with our training courses
Our interactive online courses are a great way to develop your bird identification skills, whether you're new to the hobby or a competent birder looking to hone your abilities.
Browse training coursesStatus and Trends
Population size and trends and patterns of distribution based on BTO surveys and atlases with data collected by BTO volunteers.
CONSERVATION STATUS
This species can be found on the following statutory and conservation listings and schedules.
POPULATION CHANGE
The Dartford Warbler was first recorded breeding in the UK in 1773 near Dartford and numbers have subsequently fluctuated reaching a low point of 11 pairs in the early 1960s following two successive severe winters (Tubbs 1967). Since then numbers have increased substantially with an estimate of 3,214 breeding pairs at the time of the last national survey in 2006 (Wotton et al. 2009). The breeding range has recently expanded into East Anglia, central England and Wales (Balmer et al. 2013). Numbers again fell dramatically after the severe winters of 2008/09 and 2009/10 (Clark & Eyre, 2012) and after the 'Beast from the East' in 2018 (Eaton et al. 2020). Recent figures from the RBBP suggest that the population has not yet recovered to the levels seen in 2006, with 1,450 territories counted in 2019, although this count is likely to be slightly low as coverage is incomplete (Eaton et al. 2021).
DISTRIBUTION
Breeding Dartford Warblers are confined to southern Britain, in both coastal and inland locations. The latter comprise lowland heathlands but also upland sites on the moorland fringes. Breeding abundance is greatest on heathlands in Hampshire, Surrey and Dorset. Breeding range expansion beyond southern England has been recent and rapid, including the colonisation of Wales, central England and East Anglia.
Occupied 10-km squares in UK
| No. occupied in breeding season | 149 |
| % occupied in breeding season | 4.9 |
| No. occupied in winter | 215 |
| % occupied in winter | 7.1 |
European Distribution Map
DISTRIBUTION CHANGE
From 1968–72 to 1988–91 the Dartford Warbler's range expanded by 52%. Since then it has expanded by 198%, accompanied by an increase in the proportion of occupied tetrads in core areas.
Change in occupied 10-km squares in the UK
| % change in range in breeding season (1968–72 to 2008–11) | +351.6% |
| % change in range in winter (1981–84 to 2007–11) | +448.6% |
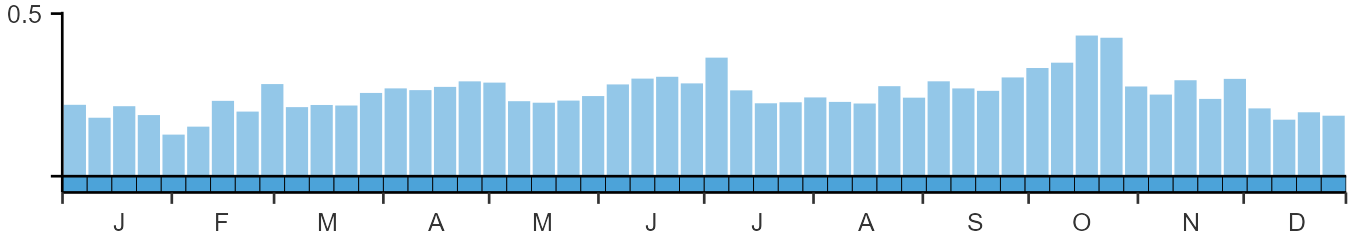
SEASONALITY
Dartford Warbler is a localised resident and recorded consistently throughout the year in suitable habitat.
Movement
Information about movement and migration based on online bird portals (e.g. BirdTrack), Ringing schemes and tracking studies.
RINGING RECOVERIES
View a summary of recoveries in the Online Ringing Report.
Biology
Lifecycle and body size information about Dartford Warbler, including statistics on nesting, eggs and lifespan based on BTO ringing and nest recording data.
SURVIVAL & LONGEVITY
View number ringed each year in the Online Ringing Report
Maximum Age from Ringing 
|
3 years 8 months 8 days (set in 1986) 
|
Typical Lifespan 
|
2 years with breeding typically at 1 year |
Adult Survival 
|
0.5±0.083  
|
BIOMETRICS
Wing Length 
|
Adults | 53.4±1.5 | Range 51–56mm, N=198 |
| Juveniles | 65.3±1.4 | Range 63-67mm, N=38 | |
| Males | 53.8±1.4 | Range 52–56mm, N=137 | |
| Females | 52.3±1.4 | Range 50–54mm, N=53 |
Body Weight 
|
Adults | 9.40±0.7 | Range 8.40–10.4g, N=173 |
| Juveniles | 12.3±1.9 | Range 9.50–16.1g, N=36 | |
| Males | 9.30±0.6 | Range 8.30–10.1g, N=120 | |
| Females | 9.60±0.8 | Range 8.50–11.0g, N=45 |
Feather measurements and photos on featherbase 
CODES & CLASSIFICATION
Ring size 
|
A |
Field Codes 
|
2-letter: DW | 5-letter code: DARWA | Euring: 12620 |
For information in another language (where available) click on a linked name
Research
Interpretation and scientific publications about Dartford Warbler from BTO scientists.
CAUSES AND SOLUTIONS
Causes of change
It is likely that loss and fragmentation of heathlands has contributed to historical declines (Wotton et al. 2009). The recent range expansion of the Dartford Warbler is likely to have been aided by climate change, which may have enabled it to occupy sites further north and also at higher altitudes (Wotton et al. 2009, Bradbury et al. 2011). However, the species also remains highly susceptible to to population crashes caused by severe winter weather (Tubbs 1967, Clark & Eyre 2012). Surviving birds following the population crash on the Thames Basin and Wealden Heaths in 2008/09 and 2009/10 were in areas containing extensive dense gorse; hence habitat management could potentially influence the severity of population crashes (Clark & Eyre 2012), although this is speculative. Short-term recovery immediately after a population crash in central western France in 2008–09 only occurred on heathland and did not occur in nearby early-growth forest habitats (Jiguet & Williamson 2013), further highlighting the importance of core heathland habitats as a factor influencing population trends for this species.
Links to more studies from ConservationEvidence.com
Would you like to search for another species?





Share this page